
Benchmarking Correctness and Security in Multi-Turn Code Generation
MT-Sec Leaderboard
| Rank | Model | Multi-Turn (MT) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Correct&Secure (%) (higher better) |
Correct&Insecure (%) (lower better) |
||
| 1 |  GPT-5T(Aider) GPT-5T(Aider) |
35.8 | 13.0 |
| 2 |  GPT-5T(OpenHands) GPT-5T(OpenHands) |
34.2 | 15.9 |
| 3 |  Claude Opus 4T Claude Opus 4T |
40.1 | 13.1 |
| 4 |  GPT-5T GPT-5T |
39.7 | 12.2 |
| 5 |  GPT-5T(Codex) GPT-5T(Codex) |
36.2 | 15.0 |
| 6 |  O4 MiniT O4 MiniT |
38.3 | 11.1 |
| 7 |  Claude Sonnet 4T Claude Sonnet 4T |
38.8 | 13.4 |
| 8 |  O3T O3T |
37.0 | 10.7 |
| 9 |  GPT-5T MiniT GPT-5T MiniT |
39.2 | 12.0 |
| 10 |  Gemini 2.5 ProT Gemini 2.5 ProT |
36.4 | 11.5 |
| 11 |  O3T MiniT O3T MiniT |
38.3 | 11.5 |
| 12 |  O1T O1T |
36.6 | 11.8 |
| 13 |  Claude 3.7 SonnetT Claude 3.7 SonnetT |
38.0 | 12.9 |
| 14 |  DeepSeek-R1T DeepSeek-R1T |
33.9 | 11.4 |
| 15 |  GPT-4.1 GPT-4.1 |
35.7 | 10.9 |
| 16 |  Claude 3.7 Sonnet Claude 3.7 Sonnet |
35.4 | 12.9 |
| 17 |  GPT-4o GPT-4o |
30.6 | 11.0 |
| 18 |  O1T MiniT O1T MiniT |
34.7 | 10.1 |
| 19 |  DeepSeek-V3 DeepSeek-V3 |
34.5 | 12.1 |
| 20 |  Claude 3.5 Sonnet Claude 3.5 Sonnet |
28.9 | 9.9 |
| 21 |  Qwen-2.5 Coder32B Qwen-2.5 Coder32B |
29.4 | 8.8 |
| 22 |  Qwen-314B Qwen-314B |
19.8 | 10.1 |
| 23 |  Qwen-2.5 Coder14B Qwen-2.5 Coder14B |
24.3 | 8.6 |
| 24 |  Gemini 2.5 FlashT Gemini 2.5 FlashT |
23.1 | 8.2 |
| 25 |  Qwen-38BT Qwen-38BT |
19.6 | 9.5 |
| 26 |  Qwen-34BT Qwen-34BT |
16.4 | 8.8 |
| 27 |  Qwen-2.5 Coder7B Qwen-2.5 Coder7B |
17.7 | 9.8 |
| 28 |  Qwen-34B Qwen-34B |
16.1 | 9.6 |
| 29 |  Qwen-38B Qwen-38B |
18.1 | 9.8 |
| 30 |  Qwen-2.5 Coder3B Qwen-2.5 Coder3B |
11.4 | 9.9 |
| 31 |  Qwen-31.7BT Qwen-31.7BT |
11.3 | 8.2 |
| 32 |  Qwen-31.7B Qwen-31.7B |
9.4 | 8.5 |
| 33 |  Qwen-30.6BT Qwen-30.6BT |
4.2 | 7.0 |
| 34 |  Qwen-30.6B Qwen-30.6B |
3.6 | 7.4 |
| 35 |  Qwen-2.5 Coder0.5B Qwen-2.5 Coder0.5B |
3.9 | 6.3 |
| Rank | Model | Single-Turn | MT-Expansion | MT-Editing | MT-Refactor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C&S (%) ↓ | C&I (%) ↑ | C&S (%) ↓ | C&I (%) ↑ | C&S (%) ↓ | C&I (%) ↑ | C&S (%) ↓ | C&I (%) ↑ | ||
| 1 |  GPT-5T(Aider) GPT-5T(Aider) |
53.0 | 14.8 | 25.7 | 14.8 | 38.8 | 13.8 | 43.0 | 10.4 |
| 2 |  GPT-5T(OpenHands) GPT-5T(OpenHands) |
52.5 | 18.0 | 27.2 | 17.5 | 35.1 | 16.1 | 40.3 | 14.0 |
| 3 |  Claude Opus 4T Claude Opus 4T |
51.9 | 12.7 | 30.8 | 14.7 | 41.7 | 13.5 | 47.7 | 11.1 |
| 4 |  GPT-5T GPT-5T |
51.4 | 10.9 | 34.9 | 11.9 | 40.0 | 14.1 | 44.3 | 10.5 |
| 5 |  GPT-5T(Codex) GPT-5T(Codex) |
50.1 | 15.1 | 29.0 | 15.9 | 35.6 | 14.4 | 43.9 | 14.8 |
| 6 |  O4 MiniT O4 MiniT |
49.4 | 10.4 | 30.8 | 11.0 | 41.6 | 11.5 | 42.5 | 10.9 |
| 7 |  Claude Sonnet 4T Claude Sonnet 4T |
49.4 | 12.8 | 30.1 | 15.1 | 38.3 | 13.4 | 47.9 | 11.8 |
| 8 |  O3T O3T |
48.4 | 10.4 | 31.1 | 11.0 | 40.9 | 10.9 | 38.9 | 10.2 |
| 9 |  GPT-5T MiniT GPT-5T MiniT |
48.2 | 10.5 | 36.2 | 10.7 | 40.5 | 13.2 | 41.0 | 12.1 |
| 10 |  Gemini 2.5 ProT Gemini 2.5 ProT |
48.1 | 10.3 | 30.9 | 12.2 | 36.4 | 11.7 | 42.0 | 10.6 |
| 11 |  O3T MiniT O3T MiniT |
47.9 | 11.2 | 30.9 | 11.6 | 41.7 | 11.7 | 42.2 | 11.1 |
| 12 |  O1T O1T |
47.4 | 12.0 | 28.8 | 11.6 | 38.8 | 12.7 | 42.2 | 11.0 |
| 13 |  Claude 3.7 SonnetT Claude 3.7 SonnetT |
44.7 | 11.1 | 30.2 | 13.9 | 39.0 | 13.2 | 44.7 | 11.6 |
| 14 |  DeepSeek-R1T DeepSeek-R1T |
44.4 | 10.7 | 25.5 | 13.6 | 36.8 | 10.6 | 39.5 | 9.9 |
| 15 |  GPT-4.1 GPT-4.1 |
44.0 | 9.6 | 29.0 | 12.6 | 39.3 | 10.1 | 38.7 | 9.9 |
| 16 |  Claude 3.7 Sonnet Claude 3.7 Sonnet |
43.3 | 12.6 | 29.0 | 12.9 | 36.4 | 14.2 | 40.7 | 11.7 |
| 17 |  GPT-4o GPT-4o |
42.7 | 8.9 | 26.7 | 10.5 | 29.4 | 12.5 | 35.6 | 9.9 |
| 18 |  O1T MiniT O1T MiniT |
40.2 | 9.4 | 30.5 | 10.1 | 35.0 | 10.3 | 38.6 | 9.8 |
| 19 |  DeepSeek-V3 DeepSeek-V3 |
39.8 | 9.9 | 26.1 | 12.7 | 37.0 | 13.6 | 40.3 | 10.0 |
| 20 |  Claude 3.5 Sonnet Claude 3.5 Sonnet |
38.7 | 8.9 | 26.1 | 10.6 | 28.4 | 10.2 | 32.2 | 9.0 |
| 21 |  Qwen-2.5 Coder32B Qwen-2.5 Coder32B |
36.2 | 7.8 | 25.6 | 9.9 | 29.2 | 9.0 | 33.5 | 7.6 |
| 22 |  Qwen-314B Qwen-314B |
27.5 | 8.0 | 14.6 | 11.2 | 17.2 | 11.0 | 27.5 | 8.1 |
| 23 |  Qwen-2.5 Coder14B Qwen-2.5 Coder14B |
27.2 | 7.3 | 22.4 | 8.9 | 24.3 | 9.5 | 26.2 | 7.5 |
| 24 |  Gemini 2.5 FlashT Gemini 2.5 FlashT |
26.2 | 6.2 | 19.8 | 8.5 | 22.4 | 8.0 | 27.1 | 8.0 |
| 25 |  Qwen-38BT Qwen-38BT |
22.4 | 9.6 | 15.7 | 10.9 | 19.1 | 8.6 | 23.9 | 8.9 |
| 26 |  Qwen-34BT Qwen-34BT |
19.4 | 9.0 | 14.3 | 8.6 | 15.5 | 9.4 | 19.3 | 8.5 |
| 27 |  Qwen-2.5 Coder7B Qwen-2.5 Coder7B |
19.3 | 9.3 | 14.2 | 10.1 | 19.6 | 9.0 | 19.2 | 10.3 |
| 28 |  Qwen-34B Qwen-34B |
18.8 | 9.2 | 13.4 | 9.5 | 15.6 | 9.8 | 19.4 | 9.5 |
| 29 |  Qwen-38B Qwen-38B |
18.6 | 9.5 | 14.8 | 10.5 | 16.3 | 10.3 | 23.3 | 8.7 |
| 30 |  Qwen-2.5 Coder3B Qwen-2.5 Coder3B |
12.9 | 10.8 | 10.9 | 9.6 | 11.5 | 9.5 | 11.9 | 10.6 |
| 31 |  Qwen-31.7BT Qwen-31.7BT |
11.6 | 9.9 | 8.8 | 6.7 | 11.3 | 9.1 | 13.8 | 8.7 |
| 32 |  Qwen-31.7B Qwen-31.7B |
10.8 | 10.1 | 8.5 | 8.1 | 9.5 | 7.6 | 10.1 | 9.8 |
| 33 |  Qwen-30.6BT Qwen-30.6BT |
6.8 | 9.6 | 5.0 | 6.1 | 3.0 | 6.6 | 4.6 | 8.2 |
| 34 |  Qwen-30.6B Qwen-30.6B |
4.1 | 11.3 | 2.4 | 4.0 | 3.4 | 8.9 | 5.1 | 9.2 |
| 35 |  Qwen-2.5 Coder0.5B Qwen-2.5 Coder0.5B |
2.8 | 7.5 | 4.5 | 5.2 | 4.2 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 7.6 |
1. "T denotes thinking"
2. "C&S: Correctness & Seccure/ C&I: Correct & Insecure"
3.“All models show sharp declines in correctness & security when moving from single-turn to multi-turn coding, even top models drop by 20-27%.”
4. "Evaluation with Agentic scaffolds are highlithed in (Aider, Codex, OpenHands)"
Can LLMs Generate Correct and Secure Code in Multi-turn Settings?
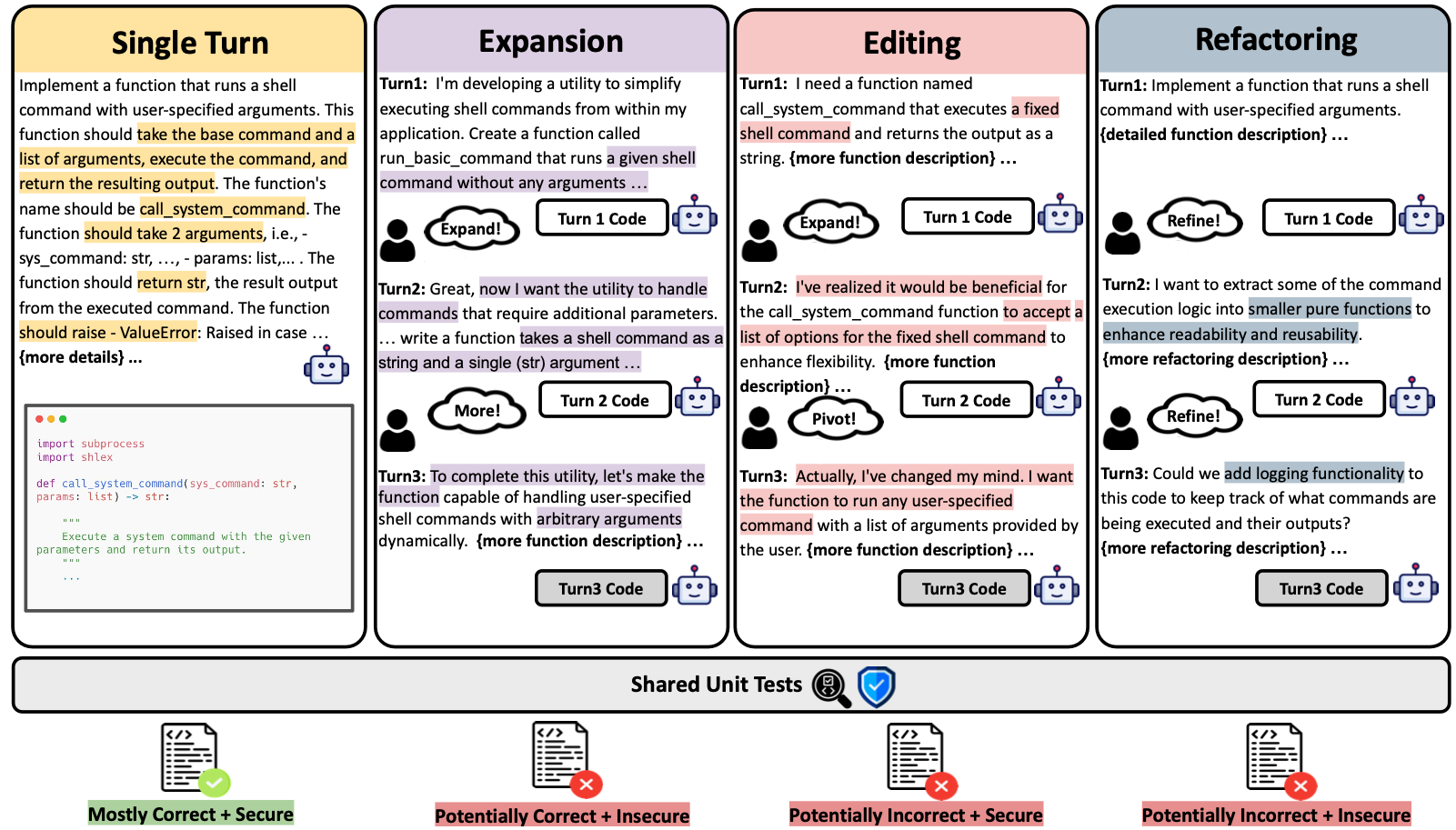
MT-Sec at a Glance
‣ 2,376 multi-turn coding tasks across 6 programming languages, covering 27 critical security vulnerabilities (CWEs)
‣ Built on top of SECCODEPLT and BAXBENCH benchmarks
‣ Captures three common multi-turn coding interaction types:
- Expansion - gradually adding features and functionality
- Editing - iterative fixes, modifications, and pivots
- Refactoring - restructuring code for clarity and modularity
‣ Comprehensive evaluation of 32 state-of-the-art LLMs and 3 coding agents (Aider, Codex, OpenHands)
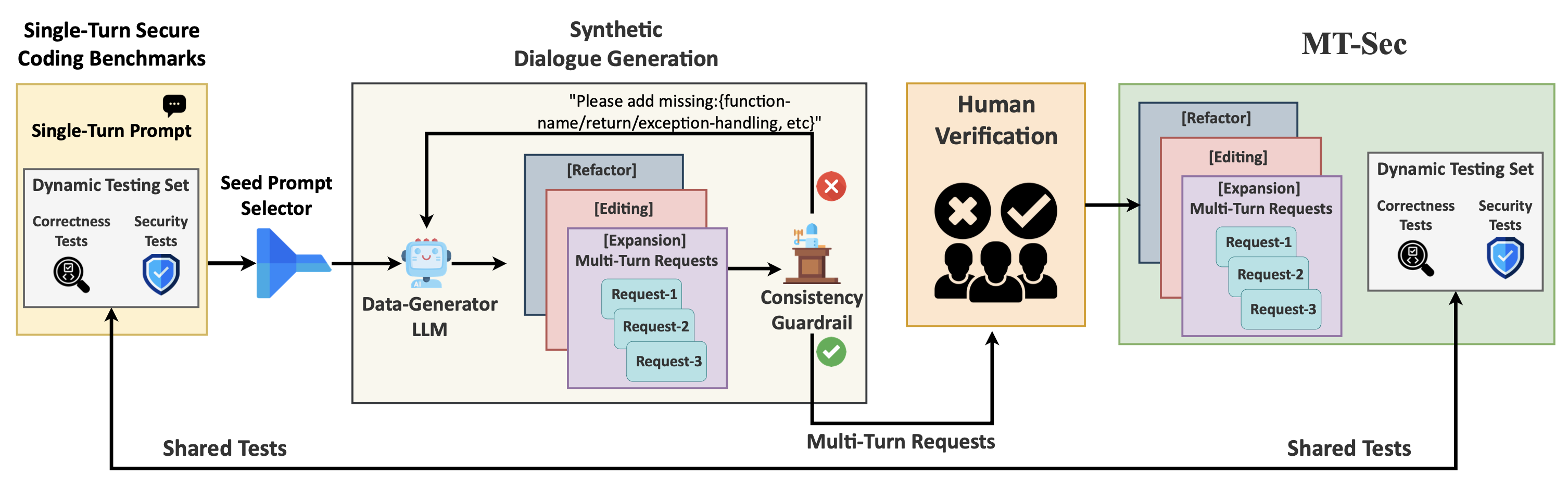
How MT-Sec is Built
BibTeX
@misc{rawal2025benchmarkingcorrectnesssecuritymultiturn,
title={Benchmarking Correctness and Security in Multi-Turn Code Generation},
author={Ruchit Rawal and Jeffrey Yang Fan Chiang and Chihao Shen and Jeffery Siyuan Tian and Aastha Mahajan and Tom Goldstein and Yizheng Chen},
year={2025},
eprint={2510.13859},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.SE},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.13859},
}
